Tetanus causes serious bacterial infections that can become life-threatening without proper treatment. Fortunately, the tetanus shot provides effective protection against this deadly disease. Yet, many people are unaware of the importance of staying up to date with their tetanus vaccinations, especially booster shots. In this article, we’ll explore why the tetanus vaccine remains essential for everyone and why regular boosters are crucial for lifelong protection.

How Tetanus Affects the Body:
The bacterium Clostridium tetani, commonly found in soil, dust, and manure, causes tetanus. Once these bacteria enter the body through a cut or puncture wound, they release a toxin called tetanospasmin. This toxin targets the nervous system, leading to severe muscle spasms, stiffness, and difficulty swallowing.
Symptoms of Tetanus:
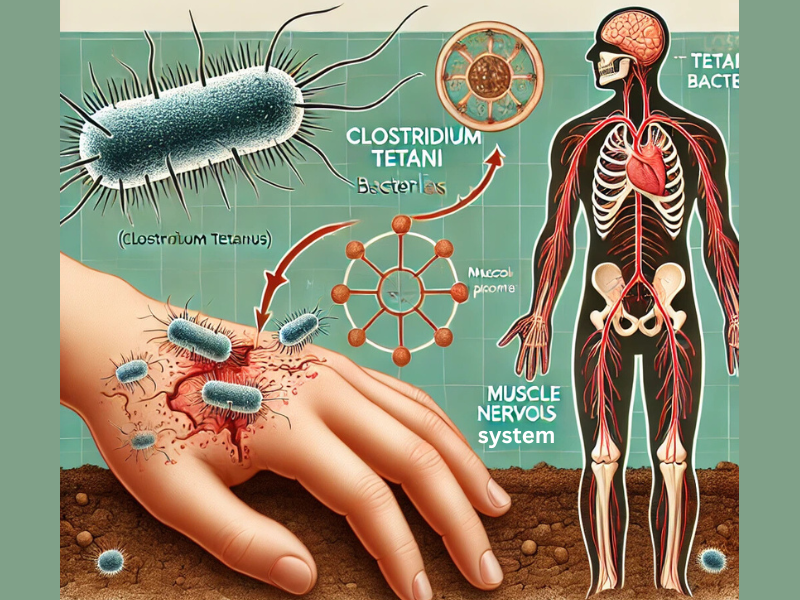
- Painful muscle stiffness all over the body
- Difficulty breathing
- Sudden, involuntary muscle spasms triggered by sound, light, or touch
- Fever and sweating
The most recognizable symptom is “lockjaw,” where the jaw muscles tighten so much that the person cannot open their mouth.
Complications of Untreated Tetanus:
If left untreated, tetanus can cause life-threatening complications, such as breathing problems, pneumonia, or even death. Fortunately, this infection is entirely preventable with the tetanus shot. Learn more about tetanus symptoms and treatment from the CDC.
Global Impact of Tetanus
Although tetanus has become rare in the United States due to widespread vaccination, it remains a significant health challenge in developing countries with lower vaccination rates. According to the World Health Organization, neonatal tetanus alone accounts for thousands of deaths annually in regions with limited access to vaccines and healthcare.
The Importance of the Tetanus Shot:
How the Tetanus Shot Protects You
The tetanus shot, also known as the tetanus vaccine, is the most effective way to prevent tetanus. It stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that fight the bacteria if they enter the body. Unlike many other infections, natural immunity to tetanus does not develop after exposure to the bacteria, making vaccination the only reliable method of protection.
Why Regular Boosters Are Necessary
The body retains long-term immunity from the vaccine, but this protection fades over time, making regular booster shots essential. Typically, these boosters are recommended every 10 years, though your doctor may advise a sooner dose in cases such as an injury that breaks the skin.
If you haven’t received a tetanus shot in years, it’s never too late to start. Whether it’s your first tetanus vaccine or a booster, ensuring your protection against tetanus is critical. Find more information about the tetanus vaccine on WebMD.
Tetanus Boosters
While many believe the tetanus vaccine is a one-time shot, regular boosters are necessary to maintain immunity. Without these boosters, the body’s ability to fight off tetanus diminishes over time. A tetanus booster, such as the Tdap vaccine (tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis), is recommended every 10 years to ensure ongoing protection.
Who Should Get the Tetanus Vaccine?
Tetanus doesn’t discriminate; it can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. That’s why it’s crucial for everyone to stay current with their tetanus vaccinations. The tetanus shot is a part of routine immunizations and should never be overlooked.
Here’s a breakdown of who needs the tetanus shot:
Children:
Healthcare providers typically administer the tetanus vaccine as part of the DTaP (diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis) series, giving children multiple doses starting at 2 months old. Completing all doses is essential to ensure full protection.
Adults:
Adults should receive a tetanus booster (Td or Tdap) every 10 years to maintain immunity. If it has been more than a decade since your last booster, it’s time to schedule one.
Pregnant Women:
Doctors recommend that pregnant women receive the Tdap vaccine during each pregnancy to protect themselves and their newborns from tetanus and pertussis (whooping cough). This is especially important because neonatal tetanus can be fatal.
Travelers:
Those planning to visit areas with low vaccination coverage should ensure their tetanus vaccinations are up to date. Many developing countries report cases of tetanus, making it essential for travelers to be prepared.
Injury-Prone Individuals:
People working in environments with higher risks of cuts or injuries, such as construction sites or farms, should stay vigilant about tetanus vaccine boosters. If you sustain an injury, consult a healthcare provider to determine whether you need a booster.
Visit VaccineFinder to locate where you can get your tetanus shot today.
Tetanus and Pregnancy:

What is Neonatal Tetanus?
Neonatal tetanus affects newborns when unclean instruments cut a baby’s umbilical cord or unsanitary practices occur during delivery. This dangerous infection can cause severe complications and even death in newborns.
How Maternal Vaccination Helps
Pregnant women protect themselves and pass immunity to their babies by receiving the tetanus vaccine. This protection shields newborns during their first few months of life, significantly reducing the risk of neonatal tetanus.
The Importance of Vaccination During Pregnancy
Vaccination campaigns in many developing countries have drastically reduced neonatal tetanus cases by targeting pregnant women. However, this infection remains a threat in areas with limited access to vaccines. Mothers safeguard their health and their baby’s health from this preventable infection by getting vaccinated during pregnancy.
If you’re pregnant, getting a tetanus vaccination is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your health and your baby’s health.
Tetanus Shot Safety and Side Effects:
Common Side Effects of the Tetanus Shot
Experts widely regard the tetanus vaccine as safe and effective. Most people experience no serious side effects after receiving it. The most common side effects include:
- Soreness, redness, or swelling at the injection site
- Mild fever
- Fatigue or muscle aches
Most symptoms, like soreness and mild fever, typically go away within a few days and are considered normal.
Serious Side Effects and Safety
People rarely experience serious side effects from the tetanus vaccine. Remember, the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks, especially when considering the life-threatening nature of tetanus.
Dispelling Myths About the Tetanus Shot
Myth: The tetanus shot is only necessary if you step on a rusty nail.
Fact: Tetanus bacteria can be found not only on rusty objects but also in soil, dust, and animal feces. Any puncture wound or cut can expose you to tetanus, regardless of the source.
Myth: You only need one tetanus shot in your lifetime.
Fact: Immunity from the tetanus vaccine diminishes over time. To stay protected, regular boosters are required every 10 years.
Learn more about the safety of the tetanus shot on WebMD.
Why You Shouldn’t Skip Your Tetanus Shot:
The Risks of Skipping Your Tetanus Booster
Skipping your tetanus booster puts you at risk of contracting a preventable and life-threatening disease. Even in developed countries, individuals who neglect their tetanus vaccinations remain vulnerable, especially after injuries that break the skin. Tetanus can develop from seemingly minor injuries, like a small cut or scrape, underscoring the importance of regular boosters.
Global Tetanus Statistics
In regions with low vaccination rates, tetanus continues to pose a significant health risk. The World Health Organization estimates that around 30,000 people contract tetanus globally each year, mostly in areas with limited access to vaccines. These figures highlight the ongoing need for widespread vaccination and the importance of staying up to date with booster shots.
Take Action Today
Keeping your tetanus vaccination current is a simple and effective way to protect yourself from this dangerous disease. Don’t wait until it’s too late—schedule your tetanus booster today with VaccineFinder.
Stay Protected: The Importance of the Tetanus Shot
The tetanus shot safeguards individuals of all ages from a potentially deadly infection, making it a critical vaccine. By getting regular boosters every 10 years, you actively maintain lifelong protection against tetanus. Whether you’re an adult due for a tetanus booster or a pregnant woman protecting your newborn, you ensure your health and safety by staying up to date with your tetanus vaccination.
Don’t skip your next tetanus shot—your health depends on it.


[…] Tetanus Shot: Why You Still Need This Essential Vaccine […]