
Article 23 of our Series “Nourishing Your Whole Self: The SaziBox Health Guide to Holistic Nutrition”
The connection between our physical and mental health is undeniable. While exercise and stress management techniques are often discussed, the role of nutrition in supporting mental well-being is gaining increasing recognition. Welcome to this article in our series where we explore the profound impact of nutrition and mental health.
We’ll delve into how food influences our mood, energy levels, and cognitive function. By understanding the science behind this connection, we can make informed choices to nourish not only our bodies but also our minds.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Two-Way Street
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system that links our gut and brain. Through a complex network of neurons, hormones, and chemicals, these two seemingly distant organs constantly interact, influencing each other’s function.
- The Microbiome’s Impact: The gut microbiome, a vast community of trillions of microorganisms residing in our digestive tract, plays a crucial role in this communication. Research suggests that gut bacteria can produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which influence mood and behaviour.
- Research Findings: Studies have shown a strong link between gut health and mental health conditions like anxiety, depression, and stress. Imbalances in the gut microbiome have been associated with increased susceptibility to these disorders.
Tips for Supporting Gut Health and Mental Well-being:
- Eat a diverse diet rich in fibre: Fiber feeds the beneficial bacteria in your gut, promoting a healthy microbiome. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet.
- Incorporate probiotics: Foods like yoghurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi contain live beneficial bacteria that can support gut health. You can also consider probiotic supplements after consulting with a healthcare professional.
- Limit processed foods and sugar: These can negatively impact the gut microbiome and contribute to inflammation, which can affect mental health.
Serotonin: The Mood Regulator
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in regulating mood, appetite, and sleep. Interestingly, about 90% of the body’s serotonin is produced in the gut. This highlights the profound connection between nutrition and mental health.
- Dietary Influence: The foods we eat can influence serotonin production. Amino acids like tryptophan, found in protein-rich foods, are precursors to serotonin. Carbohydrates also play a role by stimulating the release of insulin, which helps tryptophan reach the brain.
- Foods that Boost Serotonin:
- Tryptophan-rich foods: Turkey, chicken, eggs, cheese, nuts, and seeds.
- Complex carbohydrates: Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Read More
Tips for Boosting Serotonin Naturally:
- Enjoy a balanced diet: Include protein and complex carbohydrates at each meal.
- Don’t skip meals: Regular eating helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, supporting serotonin production.
- Get enough sunlight: Sunlight exposure can also boost serotonin levels.
Antioxidants: Protecting the Mind
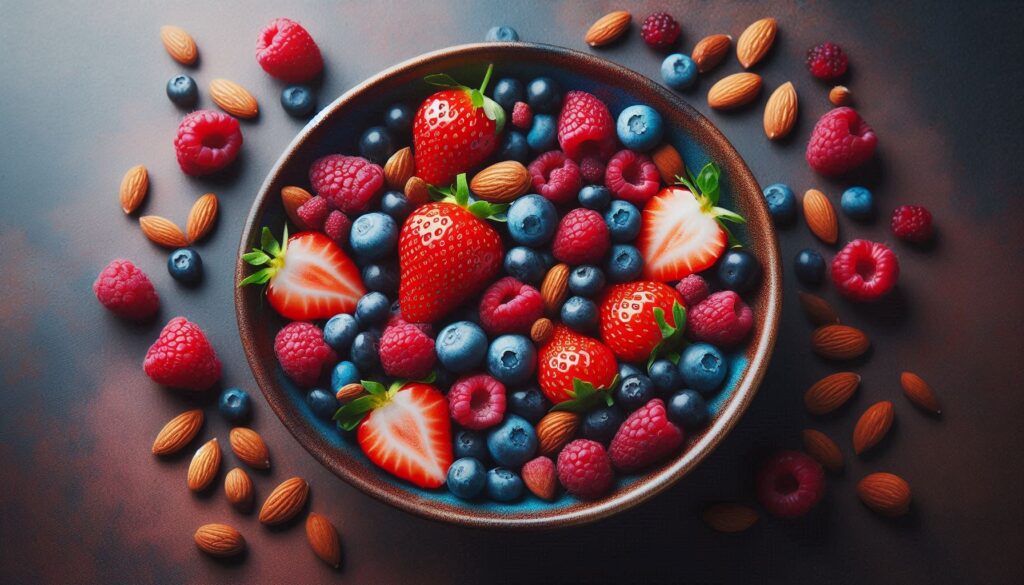

Antioxidants are compounds that protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals, and unstable molecules that can contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxidative stress and inflammation have been linked to various mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety.
- Antioxidant Powerhouses: Berries, dark chocolate, nuts, spinach, kale, and other colourful fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants.
Tip: Aim to “eat the rainbow” by including a variety of colourful fruits and vegetables in your diet each day.
Omega-3s: Essential for Brain Health
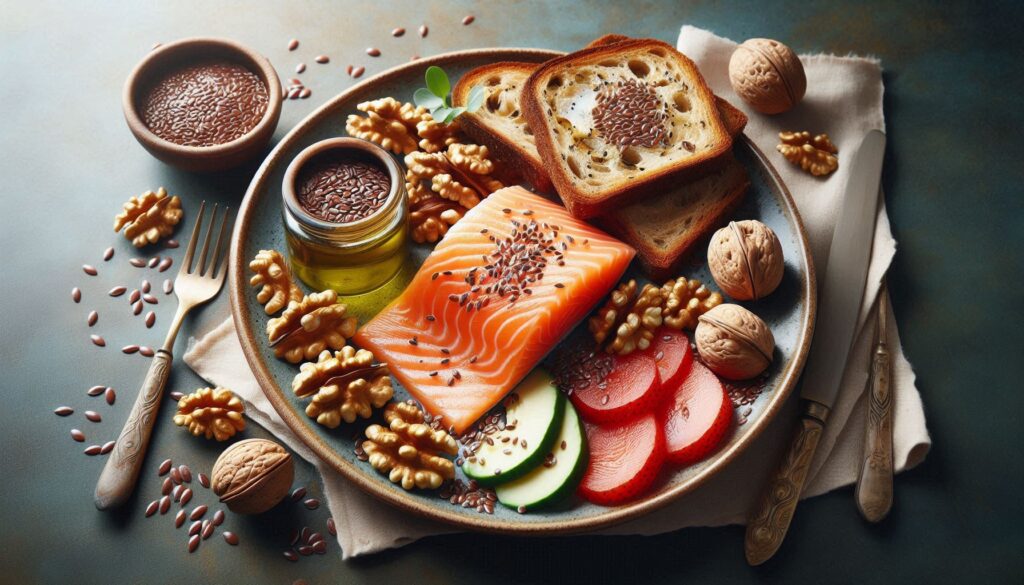

Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, are essential fats that play a crucial role in brain health. Research suggests that omega-3s can improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression, and enhance cognitive function.
- Omega-3 Rich Foods:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna
- Plant-Based Sources: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, algae oil
Tip: Aim to include fatty fish in your diet at least twice a week. If you don’t eat fish, consider a high-quality omega-3 supplement after consulting with your healthcare provider.
Nourishing Your Mind Through Food
The connection between nutrition and mental health is clear. By prioritizing a balanced diet rich in gut-friendly foods, serotonin-boosting nutrients, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids, you can support your mood, cognitive function, and overall mental well-being.
Remember, food is not just fuel for your body; it’s also nourishment for your mind.
- Share your favourite mood-boosting foods and recipes in the comments below!
- Explore the other articles in our “Nourishing Your Whole Self” series for more insights into holistic nutrition.
Let food be thy medicine, and let’s nurture our mental health, one delicious bite at a time!
References
- Firth, J., Marx, W., Dash, S., Clancy, R., Sarris, J., & Reichenberg, A. (2019). The Effects of Dietary Improvement on Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Psychosomatic medicine, 81(3), 265–280. 1. www.acamh.org www.acamh.org
- Clapp, M., Aurora, N., Herrera, L., Bhatia, M., Wilen, E., & Wakefield, S. (2017). Gut microbiota’s effect on mental health: The gut-brain axis. Clinics and practice, 7(4), 987. 1. www.crossfitinvictus.com www.crossfitinvictus.com
- Gross, C. (2017). Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Mood Disorders. In: Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S. (eds) Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Brain and Neurological Health. Springer, Cham.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional regarding any health concerns or before making any significant dietary changes.





интернет продвижение сайтов [url=http://kvartiry-na-kipre.ru/]http://kvartiry-na-kipre.ru/[/url] .
thanks
наркологическая срочная помощь [url=www.skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch11.ru]наркологическая срочная помощь[/url] .
thanks
наркологическая скорая [url=skoraya-narkologicheskaya-pomoshch12.ru]наркологическая скорая[/url] .
thanks
бизнес идея пример [url=http://biznes-idei12.ru/]http://biznes-idei12.ru/[/url] .
thanks
Вывести из запоя [url=fizioterapijakeskic.com]fizioterapijakeskic.com[/url] .
интересные идеи для бизнеса [url=https://biznes-idei13.ru/]интересные идеи для бизнеса[/url] .
thanks
Кодироваться от алкоголя в Алматы [url=https://www.kodirovanie-ot-alkoholizma-v-almaty.kz]https://www.kodirovanie-ot-alkoholizma-v-almaty.kz[/url] .
курс доллара к тенге астана [url=http://kursy-valut-online.kz/]курс доллара к тенге астана[/url] .
https://evakuator-mow.ru [url=https://evakuator-mow.ru/]https://evakuator-mow.ru/[/url] .
watch ig [url=https://anoninststories.com/]watch ig[/url] .
лечение алкогольной зависимости [url=https://xn—–7kcablenaafvie2ajgchok2abjaz3cd3a1k2h.xn--p1ai/]xn—–7kcablenaafvie2ajgchok2abjaz3cd3a1k2h.xn--p1ai[/url] .
thanks
Не знаешь, где взять деньги быстро и без отказов? Тогда заходи на [url=https://mirtinvest.ru/]mirtinvest.ru[/url]! У нас — подборка лучших МФО, готовых выдать микрозайм прямо сейчас, без лишних проверок и вопросов. Мы проверили все предложения, чтобы ты мог спокойно получить деньги на карту в любое время. Забудь про долгие ожидания — просто выбери свой займ и наслаждайся свободой!
thanks
ig viewer [url=https://www.anstoriesview.com]ig viewer[/url] .
thaanks
instagram viewer tagged photos [url=https://www.anonstoriesview.com]https://www.anonstoriesview.com[/url] .
thanks
watch stories anonymously [url=http://anon-story-view.com]watch stories anonymously[/url] .
thanks
клиника вывод из запоя ростов [url=www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov16.ru]клиника вывод из запоя ростов[/url] .
thanks
вывод из запоя дешево ростов [url=http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov15.ru]http://www.vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov15.ru[/url] .
thanks
вывод из запоя в стационаре ростова [url=https://vyvod-iz-zapoya-rostov17.ru]вывод из запоя в стационаре ростова[/url] .
thanks
Плохая кредитная история — это ещё не конец света! В 2024 году на нашем [url=https://all-credit.ru/zaym-3000-rubley/ ]сайте[/url] вы найдёте МФО, которые готовы дать вам второй шанс. Больше не нужно переживать из-за старых ошибок — займы на карту доступны даже тем, у кого кредитный рейтинг оставляет желать лучшего. На [url=https://all-credit.ru/zaim-bez-otkaza-na-kartu/ ]странице[/url] мы собрали компании, которые помогают каждому найти выход из сложной ситуации. Оформить займ легко и быстро, а главное — с верой в лучшее будущее. Дорога к финансовой свободе открыта, и она начинается прямо здесь. Верьте в свои возможности — всё обязательно получится!
thanks
Тебе больше 18 лет и срочно нужны деньги? Тогда заходи на [url=https://mirtinvest.ru/]mirtinvest.ru[/url]! У нас — подборка из более чем 40 лицензированных МФО, выдающих микрокредиты без отказов с минимальными требованиями. Ставка не выше 0,8% в день — выгоднее не найти! Не важно, кто ты и чем занимаешься — получить деньги на карту теперь легко и просто. Твой шанс здесь, не упусти его!
thanks
Если вы хотите выразить индивидуальность своему автомобилю и обновить внешний вид, то на сайте baikalwheels.ru у вас предоставляется шанс [url=https://baikalwheels.ru/catalog?type=kovanye_diski]кованые диски купить в москве[/url] лучших мировых брендов. В каталоге представлены такие бренды, как Replika, Nitro, Legeartis и K&K, которые имеют отличную репутацию. Размеры варьируются от 16 до 22 дюймов, что помогает найти идеальные диски для любых автомобилей — от седанов до внедорожников.
thanks
частный нарколог на дом [url=https://narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar17.ru/]частный нарколог на дом[/url] .
thanks
выезд нарколога на дом [url=www.narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar16.ru/]www.narkolog-na-dom-krasnodar16.ru/[/url] .
thanks
[url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]взять срочный займ на карту[/url]
Захотел денег срочно? [url=https=https://все-займы-тут.рф/]быстрый займ на карту без отказов онлайн[/url] — словно с другой планеты. Всё оформили молниеносно, деньги прилетели быстрее, чем я понял, что их потратил!
thanks
Покупай [url=https://uggs-russia.com/]угги онлайн[/url] и получай их с быстрой доставкой.
thanks
купить диплом в великих луках [url=https://orik-diploms.ru/]orik-diploms.ru[/url] .
thanks
thanks
thanks
thanks
thanks
thanks
[…] Nutrition and Mental Health: Boost Your Mood with Food […]
custom helium balloons with delivery https://helium-balloon-price.com
thanks
[…] Nutrition and Mental Health: Boost Your Mood with Food […]
[…] Nutrition and Mental Health: Boost Your Mood with Food […]