
Article 10 of our Series: Nourishing Your Whole Self: The SaziBox Health Guide to Holistic Nutrition
Welcome back to our exploration of holistic nutrition! In previous articles, we’ve covered the foundations of nutrition, the roles of macronutrients and micronutrients, the power of plant-based eating, and mindful practices. Today, we’re turning our attention to a crucial aspect of well-being: energy.
We all want to feel vibrant, focused, and ready to take on the day. While caffeine and sugar may provide a quick fix, they often lead to crashes and leave us feeling depleted. True, sustainable energy comes from nourishing your body with the right foods at the right times. Let’s dive into how you can eat for optimal energy and performance!
Balanced Meals: The Foundation of Sustained Energy

Think of your body like a car: It needs the right fuel to run smoothly. A balanced meal provides a mix of macronutrients, each playing a vital role in energy production:
- Carbohydrates: The body’s primary source of energy. Complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provide a slow and steady release of glucose, keeping your blood sugar levels stable and preventing energy crashes.
- Proteins: Essential for building and repairing tissues, proteins also contribute to satiety and help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Fats: While often demonized, healthy fats are a crucial source of sustained energy. They also help absorb fat-soluble vitamins, which play a role in energy metabolism.
Tip: Aim for a balance of all three macronutrients at each meal. A good rule of thumb is to fill half your plate with vegetables, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with complex carbohydrates. Add a small amount of healthy fats, like a drizzle of olive oil or a handful of nuts.
Nutrient Timing: Eating for Peak Performance

When you eat is just as important as what you eat. Strategic nutrient timing can help you maximize your energy levels, especially when it comes to exercise:
- Pre-workout: Focus on easily digestible carbohydrates for quick energy and a small amount of protein for muscle support.
- Post-workout: Prioritize protein for muscle repair and recovery, along with some carbohydrates to replenish glycogen stores.
- Throughout the day: Eat regular meals and snacks every 3-4 hours to avoid blood sugar dips and maintain steady energy levels.
Tip: Experiment with different timing strategies to find what works best for your body and schedule.
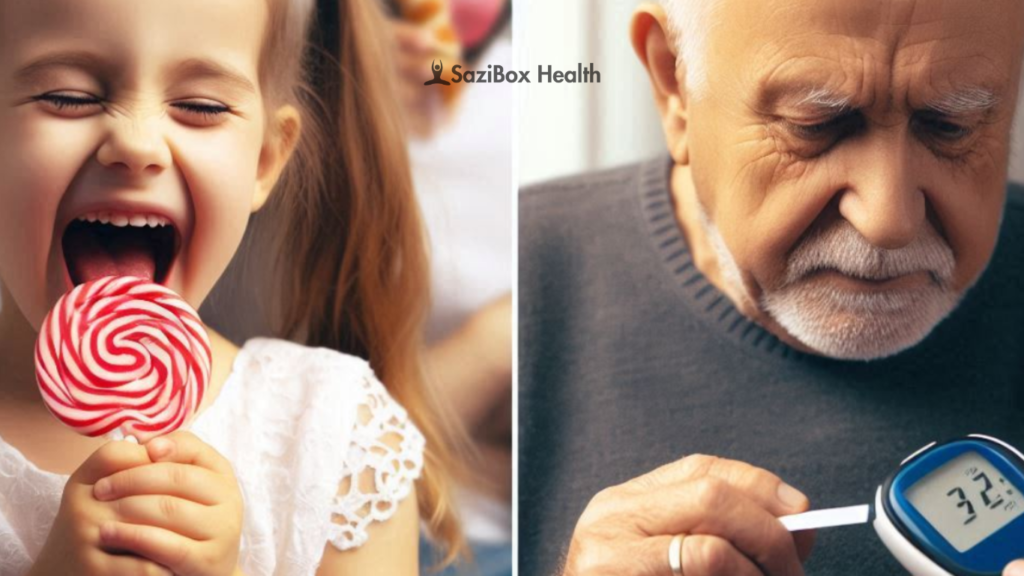
Blood Sugar Regulation: The Key to Stable Energy
Blood sugar (glucose) is your body’s primary fuel source. When blood sugar levels drop, you may experience fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. When they spike too high, you may feel jittery or experience a subsequent crash.
Tips for Maintaining Stable Blood Sugar:
- Choose low-glycemic index (GI) foods: These foods release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, providing sustained energy. Examples include whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables.
- Incorporate fibre into your meals: Fiber slows down the absorption of sugar, preventing blood sugar spikes.
- Avoid sugary drinks: These can cause rapid blood sugar fluctuations and contribute to energy crashes.
- Eat regular meals and snacks: Avoid skipping meals or going long periods without eating.
Read more
Interactive Quiz:
- Blood Sugar Savvy: Test your knowledge about blood sugar and energy with our quick quiz!
Energy-Boosting Foods: Nature’s Powerhouses
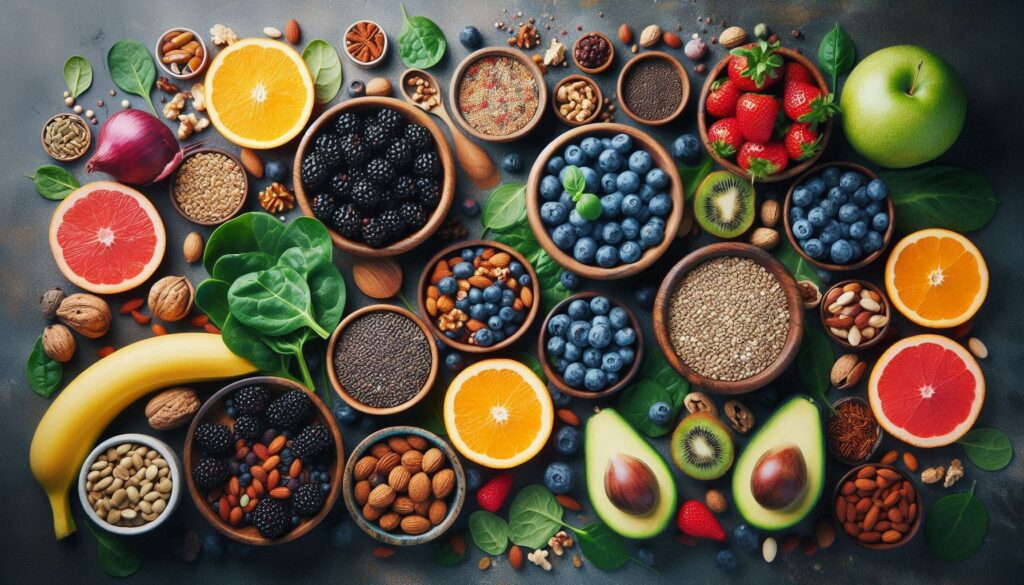

Certain foods are packed with nutrients that support energy production and combat fatigue.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Oats, brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, whole-wheat bread
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, eggs
- Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil
- Micronutrients:
- B Vitamins: Essential for converting food into energy. Found in whole grains, leafy greens, and legumes.
- Iron: Necessary for red blood cell production and oxygen transport. Found in lean meats, spinach, and lentils.
Eating for Energy is a Lifestyle
Eating for energy is not just about choosing the right foods; it’s about creating a sustainable lifestyle that supports your overall well-being. By focusing on balanced meals, strategic nutrient timing, and blood sugar regulation, you can unlock your body’s natural energy potential and feel your best throughout the day.





[…] Eating for Energy: Fuel Your Body for Optimal Performance […]
You are a very clever person!
thanks
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
thanks